Molecules bind together by sharing electrons.
For example, each oxygen atom shares electrons with two hydrogen atoms in water. The sharing of electrons makes water molecules stable.
Some molecules, called free radicals, have an unpaired electron. This makes them very unstable and highly reactive. They will tend to bind quickly with other molecules to become more stable.
Free Radicals In Your Body
As your body metabolizes all the various materials, you are exposed to—such as food, sunlight, and pollution—it produces a type of free radical known as reactive oxygen species. This is a normal byproduct of cellular metabolism.
Unfortunately, these reactive oxygen species can cause a lot of damage to your cells and their DNA. This is a condition known as oxidative stress.
Oxidative stress has been linked to the development of many chronic diseases, such as heart disease, cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, and diabetes.
Antioxidants to the Rescue
Fortunately, your body has a built-in defense system against oxidative stress. This system is made up of vitamins, enzymes, and other molecules that scavenge for free radicals and neutralize them.
These molecules are known as antioxidants.
There are many different types of antioxidants, but some of the most important ones include vitamins C and E, beta-carotene, and flavonoids.
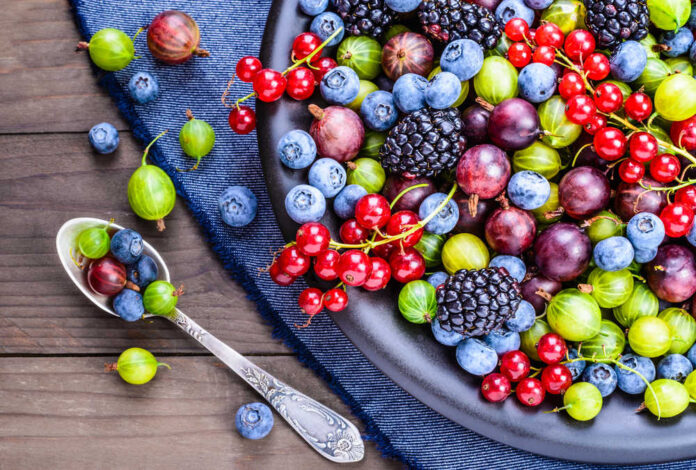
You mostly get antioxidants from the foods you eat. Fruits, vegetables, nuts, whole grains, and other plant-based foods are all particularly good sources of antioxidants.
These helpful antioxidants are one of the primary reasons why eating a healthy diet with plenty of vegetables and produce is so important.
If you aren’t getting enough antioxidants, your cells and tissues will likely become damaged by the reactive oxygen species produced by your body.
On the other hand, dietary approaches that focus on maximizing your intake of antioxidant-rich foods have been consistently demonstrated to improve your health and reduce your risk of chronic disease.
Should You Take Antioxidant Supplements?
Since antioxidants are important for maintaining and improving your health, you may wonder if you should take antioxidant supplements.
Unfortunately, there is no clear evidence that antioxidant supplements provide any benefits. This may be because the antioxidants become less efficiently absorbed and utilized when they are extracted from foods and taken in pill form.
Antioxidant supplements may also provoke negative effects by interfering with the body’s normal mechanisms for dealing with oxidative stress, especially if taken in higher doses.
For these reasons, it is generally recommended to get your antioxidants from whole foods instead of supplements. This way, you can also get all the other essential nutrients that these foods provide as well.