Bruising easily is a phenomenon that catches many off guard, leading to a mix of concern and curiosity about the underlying causes.
While bruises are common results of bumps and falls, frequent or unexplained bruising can serve as a window into the body’s internal workings, hinting at various health conditions, nutritional deficiencies, or lifestyle factors that deserve closer attention.
Understanding Bruising
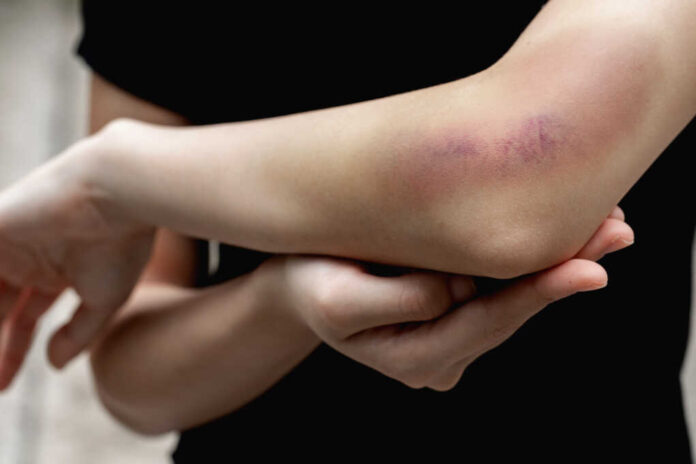
Bruises, or contusions, occur when small blood vessels under the skin break due to trauma, allowing blood to leak into the surrounding tissues.
This process results in the familiar black-and-blue marks that gradually change color as they heal.
However, when bruises appear frequently or without clear cause, it’s essential to explore the reasons behind this sensitivity.
Aging Skin
As the body ages, the skin tends to become thinner and lose some of the protective fatty layers that help cushion blood vessels from injury. This natural aging process means that even minor bumps can lead to bruising.
Older adults may also experience increased bruising due to the cumulative effects of a lifetime of sun exposure, which further weakens skin integrity.
Medication Effects
Certain medications can contribute to easy bruising. Blood thinners like aspirin, warfarin, and clopidogrel are designed to prevent blood clots, but they also make it easier for bruises to form by reducing the blood’s ability to clot.
Similarly, steroids, both systemic and topical, can thin your skin, making it more prone to bruising.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Nutrition and diet influences skin health and blood clotting. Deficiencies in vitamins C and K, for example, can lead to increased bruising.
Vitamin C is involved in the synthesis of collagen, an essential component of blood vessel walls and skin. A lack of vitamin C weakens these structures, making them more susceptible to bruising.
Vitamin K is critical for blood clotting ― without enough of it, even minor injuries may lead to more significant bleeding and bruising.
Underlying Health Conditions
Easy bruising can also indicate more serious underlying health issues.
Conditions such as liver disease, kidney disease, or certain blood disorders like hemophilia or leukemia can impair the body’s ability to clot blood, leading to more frequent or severe bruising. These conditions often require comprehensive medical evaluation and management.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices, including alcohol consumption and intense physical activity, can influence bruising. Alcohol tends to have a thinning effect on the blood and may exacerbate liver conditions, both of which can increase bruising.
High-intensity exercises and contact sports increase the risk of trauma to the body, naturally leading to more bruises.
Preventive Measures and When to Seek Help
While some factors contributing to easy bruising can be addressed with lifestyle adjustments or dietary changes, don’t overlook the importance of medical advice.
If bruising is frequent, appears without cause, or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms such as excessive bleeding or unexplained pain, seeking medical evaluation is needed. This step ensures that any serious conditions are identified and managed promptly.
Understanding the various reasons behind easy bruising empowers individuals to take proactive steps in addressing potential health concerns. It underscores the body’s way of signaling the need for care, whether through adjustments in medication, diet, or the investigation of underlying health issues.
Ultimately, acknowledging and responding to these signs is a vital component of maintaining overall health and well-being.