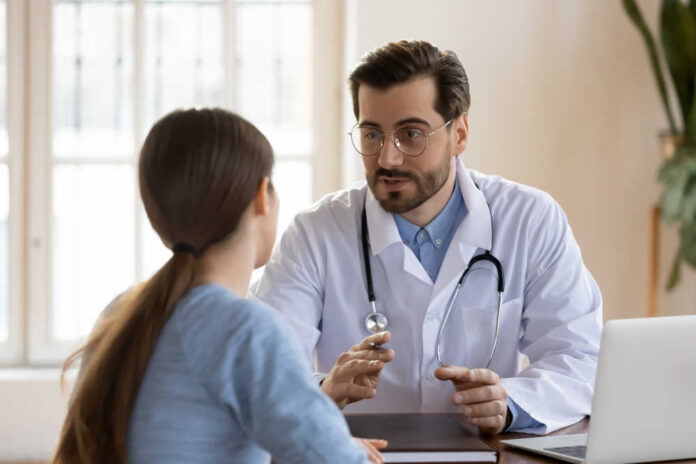
Over half of American adults take at least one prescription medication, and many of these take two or more.
You may not give much thought to how you take your pills. It only takes a moment, and you probably go through the same routine every time.
But it’s worth considering whether this routine is the most effective way to take your medication. You may be accidentally reducing the effectiveness of your pills or increasing your risk of side effects.
Here’s a look at the science behind taking pills and some tips on how to get the most out of your medication.
Follow The Instructions
First and foremost, it’s important to follow the instructions that come with your medication.
The directions on the bottle or package insert are there for a reason. They’re based on extensive research and are designed to ensure that you safely get the most benefit from your medication.
For example, some pills need to be taken with food while others should be taken on an empty stomach. You may need to avoid mixing with alcohol or certain foods. Taking a pill incorrectly can reduce its effectiveness or cause unwanted or dangerous side effects.
Have a conversation with your doctor or pharmacist about timing, dosage, duration, and other important factors for taking your medication. Ask questions if you’re unsure about anything.
Suppose you’ve been taking a medication for an extended period of time. In that case, you should still review the instructions periodically in case any information has changed or in case you may have drifted away from proper usage.
Don’t Skip Doses
You may be tempted to skip a dose of your medication if you’re feeling better. But unless your doctor tells you to do so, you should take your medication as prescribed.
Many medications need to be taken on a regular schedule to be effective. Skipping doses can reduce the effectiveness of your medication and cause your condition to worsen.
If you have trouble remembering to take your medication, ask your doctor or pharmacist for suggestions. They may be able to offer tips on setting up a pill box or using a phone app to remind you.
Drink a Glass of Water With Your Pills
Unless your doctor or pharmacist specifically instructs otherwise, you should always drink a glass of water with your pills. Not just a small sip either—aim for a full glass. Drink some water, take the pill, then drink the rest.
This simple step will help ensure that your pill reaches your stomach and doesn’t get stuck in your throat. It will also help to prevent indigestion or heartburn that could come from taking a dry pill.
Don’t Lie Down
Recent research has demonstrated that your posture when taking oral medication (and immediately after) can have a big impact on how well the medication is absorbed.
Sitting or standing upright is best.
Lying down can reduce how quickly and efficiently the medication passes from your stomach to your intestines (where it is absorbed into your bloodstream). You may end up with a lower blood concentration of the medication as a result.
The worst posture appears to be lying on your left side. Since your intestines connect to the lower right side of your stomach, this position can hold the medication in your stomach and prevent it from reaching your intestines promptly.
If you are bedridden or have trouble sitting or standing, talk to your doctor about the best way to take your medication.
Know When It’s OK To Stop
Follow your doctor’s instructions regarding when to stop taking your medication. Even if you are feeling better, there may still be something going on inside your body that the medication is treating. Stopping too early can cause a relapse of your illness or worsen your condition.
Some medications must be tapered off gradually, while others can be stopped abruptly. Your doctor will give you specific instructions. Ask questions if you’re unsure.
If you have been taking a medication for an extended period, consult with your doctor about whether you can reduce the dosage or eventually stop taking it.
Never change the dosage or stop taking a medication without first talking to your doctor.