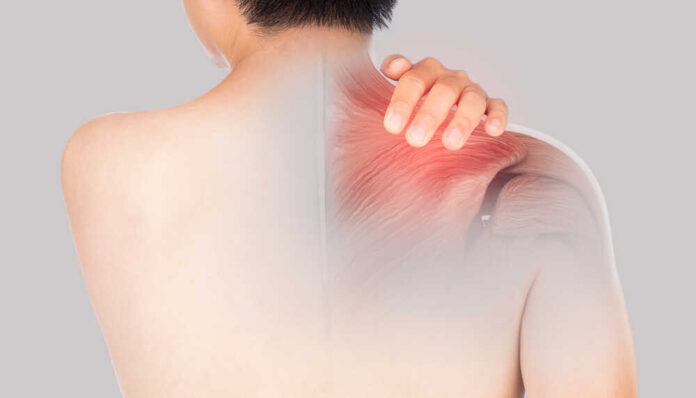
Inflammation is the body’s immune response to injury, infection, or irritation. It’s a protective measure that helps remove harmful substances, such as pathogens, damaged cells, and irritants, from the body.
Inflammation can be both beneficial and harmful, depending on the circumstances.
Acute Inflammation
Acute inflammation is a minor, temporary, and short-term response that usually occurs within minutes to hours of an injury or infection. It’s generally characterized by redness, heat, swelling, and pain.
The primary function of acute inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of injury and restore tissue function. This is a vital process that helps us heal and stay healthy.
Chronic Inflammation
But when inflammation is severe and long-lasting, it can cause all sorts of problems in our bodies.
Chronic inflammation is a long-term inflammatory response that can last for months or even years or decades. It’s typically caused by persistent infections, autoimmune disorders, unhealthy habits, or long-term exposure to irritants.
Chronic inflammation can damage healthy tissues, leading to various health issues such as heart disease, cancer, and arthritis.
Causes of Inflammation
Inflammation can be triggered by a variety of factors, including:
- Infections: Bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens can cause inflammation as the body tries to eliminate the infection.
- Injuries: Physical trauma, such as cuts, burns, or fractures, can result in inflammation to help the healing process.
- Autoimmune disorders: Conditions like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, causing inflammation.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to irritants like pollution, chemicals, or allergens can lead to inflammation.
Symptoms of Inflammation
Inflammation can manifest in many ways, but common symptoms include:
- Redness
- Swelling
- Heat
- Pain
- Itchiness
- Loss of mobility or function (in severe cases)
Chronic inflammation may not always cause noticeable symptoms, but it can still damage the body over time.
Treating Inflammation
The treatment of inflammation depends on its cause, severity, and duration. Common approaches include:
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or aspirin can help reduce pain and inflammation. Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are also used to treat more severe cases of inflammation.
- Rest and immobilization: Resting the affected area and avoiding activities that could worsen inflammation can aid in the healing process.
- Ice and heat: Applying ice to an inflamed area can help reduce swelling and pain, while heat can increase blood flow and promote healing.
- Physical therapy: In some cases, physical therapy may be recommended to help regain function and mobility in the affected area.
Prevention and Lifestyle Choices
Preventing inflammation involves adopting a healthy lifestyle, which includes:
- Eating a balanced diet: Consume a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy plant-based fats. Anti-inflammatory foods, such as berries, leafy greens, fatty fish, and nuts, are especially good at reducing inflammation in the body.
- Exercising regularly: Engaging in moderate exercise for at least 150 minutes per week can lower inflammation and improve overall health.
- Managing stress: Chronic stress can contribute to inflammation. Practice stress-reduction techniques, such as mindfulness, creative art, spending time in nature, or therapy, to help manage stress levels.
- Getting enough sleep: Aim for consistent, high-quality sleep every night to support your immune system and reduce inflammation.
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption: Tobacco and alcohol can increase inflammation in the body. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Obesity is closely associated with chronic inflammation. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce inflammation and lower the risk of related health issues.
When to See a Doctor
While inflammation is often a natural part of the healing process, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional if you experience:
- Severe pain or swelling
- Persistent inflammation that lasts longer than a few days
- Signs of infection, such as fever, chills, or pus
- Chronic inflammation that affects your quality of life or daily activities
In these cases, a healthcare professional can help determine the cause of inflammation and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan.