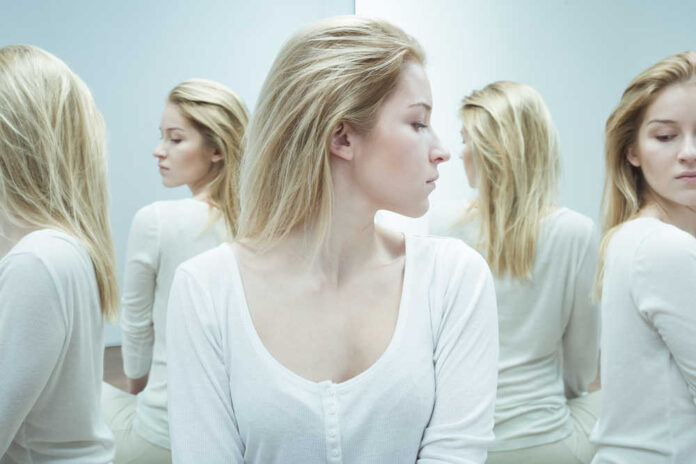
Schizophrenia is a mental health condition that affects 1% of people in the United States.
While schizophrenia is commonly associated with symptoms like hearing voices, complex hallucinations, and paranoia, it can manifest more subtly.
The symptoms of schizophrenia are often delineated into positive and negative symptoms—things that you have and things that you are missing.
Positive Symptoms of Schizophrenia
Positive symptoms refer to the presence of behaviors, thoughts, and emotions that are not typically found in healthy individuals.
There are three basic types of positive symptoms that a person with schizophrenia may have:
● Delusions
● Hallucinations
● Incoherence
Delusions are false beliefs that have little or no basis in reality. Common forms of schizophrenic delusions include:
● Delusions of grandeur – feeling that you are more important or powerful than you actually are
● Persecutory beliefs – feeling that someone is out to get you or harm you
● Paranoid delusions – believing you are being followed or watched by conspiratorial powers
● Religious delusions – beliefs centered around religious themes or figures
● Nihilistic delusions – believing you don’t exist or that reality is not real
Hallucinations involve sensing something that isn’t actually present. This can be seeing, hearing, feeling, or even smelling or tasting things that are not there. Common forms of hallucinations include:
● Auditory hallucinations – Hearing voices or other sounds that are not real
● Visual hallucinations – Seeing people, objects, and landscapes that do not exist
● Tactile hallucinations – Feeling sensations on your skin like bugs crawling or something touching you
Incoherence may also be termed disorganized speech or disordered thinking. This occurs when a person’s thoughts and sentences do not make sense or they jump quickly from one topic to the next. This can make communication difficult, as it is hard to understand the meaning of what is being said.
Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia
Negative symptoms refer to the absence of certain behaviors that would otherwise be expected from a healthy individual. These signs may not be as obvious as positive symptoms since they signify something that is not there rather than something that is there. Examples of negative symptoms may include:
● Social withdrawal – avoiding contact or conversation with people, including family and friends
● Lack of motivation – failing to take the initiative or show enthusiasm
● Lack of energy – feeling tired or fatigued even after getting enough sleep
● Lost passion – without joy or pleasure in life
● Flat affect – having a very limited range of emotions
● Catatonia – a state of unresponsiveness, as if they are frozen or in a trance
● Lack of sleep – sleeping too little or too much
● Lack of self-care – ignoring basic needs like bathing, grooming, and eating
● Cognitive impairment – inability to concentrate, learn, remember, or make decisions
Other Signs of Schizophrenia
In addition to the positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia, there are some additional considerations that a doctor may take into account when making a diagnosis:
● Duration – the symptoms must have been present for more than six months
● Functioning – the person’s day-to-day functioning has been impaired
● Distress – the person is experiencing distress or difficulty due to their symptoms
● Rule out other causes – symptoms are not caused by substance abuse or another mental health condition
● Severity – schizophrenia is described as a spectrum, and the severity of symptoms can vary from person to person.
Schizophrenia is a complex and serious mental health condition that can greatly affect a person’s life, as well as the people around them. It is important to seek professional help if you or someone you know may be experiencing the signs and symptoms of schizophrenia.
Although there is no known cure for schizophrenia, treatment options are available and can help reduce the severity and frequency of symptoms.