While it’s no secret that minerals play a significant role in skin health, magnesium often takes a back seat to other nutrients like zinc or vitamin C.
Magnesium, an essential mineral, plays a vital role in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body, including those related to skin health—protein synthesis, cellular energy production, and maintaining the integrity of the skin barrier, for example.
A deficiency in magnesium can contribute to a host of skin problems, including dryness, inflammation, and signs of aging.
Combating Inflammation
Inflammation is one of the leading causes of various skin issues, including acne, rosacea, and eczema.
Magnesium may help reduce inflammation by counteracting the effects of calcium, which can sometimes overstimulate the nerves and muscles, leading to increased inflammation.
Magnesium also supports a healthy immune system, which can help protect your skin from harmful bacteria and infections.
Promoting Collagen Production
Collagen is a protein that provides strength and elasticity to your skin, making it look younger and smoother.
As you age, your collagen production declines, leading to wrinkles and sagging.
Magnesium plays a vital role in the synthesis of collagen by acting as a cofactor in the enzymatic process. Ensuring adequate magnesium levels helps maintain healthy collagen production and keeps your skin looking youthful.
Enhancing Hydration and Reducing Dryness
Dry, flaky skin can not only be uncomfortable but also contribute to aging and other skin issues.
Magnesium aids in maintaining your skin’s natural moisture barrier, which helps retain moisture and prevents dryness. Magnesium can also help regulate the production of sebum, the oil that keeps your skin lubricated and hydrated.
Skin Repair and Regeneration
Your skin undergoes constant repair and regeneration to maintain its health and appearance.
Magnesium plays a key role in the process of cell division and the synthesis of proteins, including those responsible for repairing damaged skin tissue.
By supporting healthy cell division, magnesium ensures the timely renewal and regeneration of your skin.
Reducing Stress-Related Skin Issues
Stress can wreak havoc on your skin, contributing to acne breakouts and premature aging.
Magnesium is known as the “relaxation mineral” because it helps regulate neurotransmitters that influence your stress response. By helping to manage your stress response and by promoting relaxation, magnesium can help improve your overall skin health and appearance.
How to Get More Magnesium
Here are some ways to increase your magnesium intake:
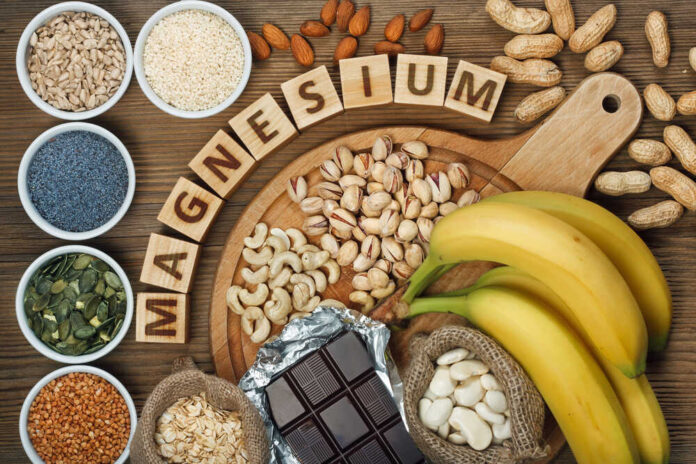
- Eat magnesium-rich foods: Include a variety of magnesium-rich foods in your diet, such as dark leafy greens, nuts, seeds, legumes, whole grains, avocados, bananas, and dark chocolate.
- Take supplements: If you’re unable to get enough magnesium through your diet, consider taking a magnesium supplement. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage and form of magnesium supplement for your needs.
- Use topical magnesium products: Magnesium can also be absorbed through the skin. Try using magnesium-based skincare products, such as magnesium-infused creams, lotions, or oils. Magnesium oil can also be used as a spray or added to bathwater for a relaxing soak.
- Epsom salt baths: Epsom salt (magnesium sulfate) is known for its ability to relieve muscle aches and promote relaxation. Add Epsom salt to your bathwater and soak for 20-30 minutes to help your body absorb the magnesium and experience its benefits.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, managing stress, and staying well-hydrated can all contribute to maintaining adequate magnesium levels in your body.
Consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your diet or supplement routine, especially if you have any pre-existing health conditions or are taking medications. They can help ensure you are consuming the right amount of magnesium and monitor for any potential interactions or side effects.