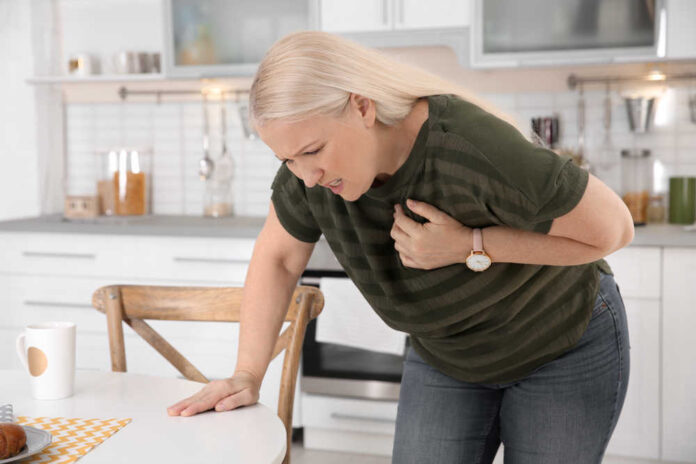
A stroke is a severe medical emergency when the blood flow to your brain is interrupted.
It is one of the leading causes of death and disability worldwide. In the United States alone, someone has a stroke every 40 seconds, on average.
Despite its prevalence, there is still a lot of misinformation about strokes. Here are five of the most common myths:
MYTH #1 : Strokes Only Happen to Older Adults
Your risk of having a stroke does increase as you get older, but strokes can happen to people of any age.
Approximately 38% of strokes happen to people under the age of 65. And 15% of ischemic strokes happen to adolescents and young adults.
Risk factors such as high blood pressure, obesity, and smoking may be more significant contributors to the development of strokes than your age.
MYTH #2 : Strokes Cannot Be Prevented
There are many known risk factors for strokes. Some of these are things you have no control over, such as:
- Genetics
- Family history
- Ethnicity
- Sex
- Age
But there are also many risk factors that you do have some control over. These modifiable risk factors include:
- High blood pressure
- Cigarette smoking
- Lack of physical activity
- Type 2 diabetes
- Alcohol intake
- Psychosocial stress
- Depression
Each of these factors can be addressed with lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet, quitting smoking, and exercising regularly.
MYTH #3 : Strokes Always Have Obvious Symptoms
Everyone should memorize the FAST acronym as a reminder of the most common symptoms of strokes:
- F – Face drooping – If the person smiles, does one side of the face droop?
- A – Arm weakness – Can they raise their arms? Is one arm weak or numb?
- S – Speech difficulty – Is their speech slurred? Are they confused? Can they repeat a simple sentence back to you correctly?
- T – Time to call 911 – If you see any of these signs, it’s time to call for emergency medical help.
Knowing these warning signs can help you get the person emergency medical attention as soon as possible.
However, it’s important to remember that not all strokes present these symptoms. In some cases, people may only experience a headache or dizziness.
Silent strokes (strokes with no obvious symptoms) are even more common than strokes with symptoms. These are often not even noticed until scar tissue is found in an MRI scan sometime in the future. But that doesn’t mean they’re not serious. Silent strokes can still cause damage to the brain and lead to long-term problems.
MYTH #4 : A Stroke is Not an Emergency
When someone is having a stroke, every second counts.
The sooner the person gets medical attention, the better the chances are that the person will survive and recover.
If you think that you or someone around you is having a stroke, call 911 immediately. Don’t wait to see if the symptoms go away.
MYTH #5 : You Can’t Recover From a Stroke
A stroke is not necessarily a death sentence. With prompt medical treatment and rehabilitation, many patients can recover fully or partially.
Although it may not always be possible to recover fully, most people will only experience minor or moderate impairments after a stroke.
The first few days and the following three months after a stroke are the most crucial for recovery. But rehabilitation and therapy can continue for many more months or even years after a stroke.
If you or someone you know has had a stroke, don’t give up hope. Treatment and recovery strategies continue to evolve and improve as more is learned about strokes.
Talk to your doctor or healthcare team about any questions or concerns. They can help clear up any confusion or misconceptions about strokes.